
Australian Skilled Visa Processing Priorities
In this column, we will have a look at the new processing priorities for skilled visa applications the Department of Home Affairs introduced on 28 October 2022. These applications are to be processed according to the Ministerial Direction No. 100 order of consideration.
The priority processing order for visa applications:
1. Visa applications related to Healthcare or Teaching Occupations (see below)
2. Visa applications where applicant is nominated by an Approved sponsor with Accredited Status
3. Visa applications related to an occupation in a designated regional area
4. Visa applications that count towards the migration program (excluding certain visas)
5. All other visa applications
Within each of the above categories, priority is given to visa applications made by offshore applicants at time the application is made as well as to the holder of eligible passports. These passports include Hong Kong Special Administrative Region of the People’s Republic of China passports and British National (Overseas) passports.
All other skilled visa applications are assessed in order of date of lodgement.
Healthcare or Teaching Occupations refer to occupations in any of the following groups:
- ANZSCO Sub-major Group 25 – Health Professionals
- ANZSCO Minor Group 241 – School Teachers
- ANZSCO Minor Group 411 – Health and Welfare Support Workers
- ANZSCO Unit Group 1341 – Child Care Centre Managers
- ANZSCO Unit Group 2346 – Medical Scientists
- ANZSCO Unit Group 2721 – Counsellors
- ANZSCO Unit Group 2723 – Psychologists
- ANZSCO Unit Group 2725 – Social Workers
- ANZSCO Unit Group 3112 – Medical Technicians
ANZSCO occupations:
- 134311 – School Principal
- 421111 – Child Care Worker
- 423111 – Aged or Disabled Carer
- 423312 – Nursing Support Worker
- 423313 – Personal Care Assistant.
The relevant skilled visas which are impacted include the following:
- Subclass 124 (Distinguished Talent)
- Subclass 186 (Employer Nomination Scheme)
- Subclass 187 (Regional Sponsored Migration Scheme)
- Subclass 188 (Business Innovation and Investment) (Provisional)
- Subclass 189 (Skilled – Independent)
- Subclass 190 (Skilled – Nominated)
- Subclass 191 (Permanent Residence (Skilled Regional))
- Subclass 457 (Temporary Work (Skilled))
- Subclass 482 (Temporary Skill Shortage)
- Subclass 489 (Skilled – Regional (Provisional))
- Subclass 491 (Skilled Work Regional (Provisional))
- Subclass 494 (Employer Sponsored Regional (Provisional))
- · Subclass 858 (Global Talent)
- Subclass 887 (Skilled – Regional)
- Subclass 888 (Business Innovation and Investment (Permanent)
If your occupation falls under any of the Healthcare and Teaching Occupations referred to by the Ministerial Direction No. 100, any new skilled visa application submitted to the Department of Home Affairs will be fast-tracked and prioritized for assessment in line with the local demand for skilled workers within these critical sectors.
It is important to submit all required documents and applications as soon as possible to avoid delays in processing.
For more information, please contact Mosaic Migration & Education.

QLD – Fee waivers for dependent students of Temporary Visa holders
This column will look at the tuition fee exemptions for eligible dependent students of temporary visa holders.
Among the many reasons for coming to Australia, the biggest reason is children’s education. And If you are a temporary visa holder with children, many people are curious about the tuition exemption for their children.
This is critical information because if your child does not receive a tuition waiver or discount, the tuition for primary school students is $14,192 (Tuition Fee for 2023), which can be a big burden. While not all temporary visas get exempt, most public schools offer tuition exemptions or reduced tuition for private schools.
However, it is essential to look at each State’s education website as there are differences in tuition fees and visas.
Tuition exemption visas for under-age children of the main application are as follows:
| Subclass | Visa Title |
| 159 | Provisional Resident Return |
| 173 | Contributory Parent |
| 188 | Business Innovation and Investment (Provisional) |
| 300 | Prospective Marriage |
| 309 | Partner (Provisional) |
| 400 | Temporary Work (Short Stay Activity) |
| 403 | Temporary Work (International Relation) |
| 407 | Training |
| 408 | Temporary Activity |
| 444 | Special Category Visa |
| 445 | Dependent Child |
| 449 | Humanitarian Stay (Temporary) |
| 461 | New Zealand Citizen Family Responsibility (Temporary) |
| 476 | Skilled – Recognised Graduate |
| 482 | Temporary Skill Shortage (previously 457) |
| 485 | Temporary Graduate |
| 489 | Skilled Regional (Provisional) |
| 491 | Skilled Regional (Provisional) |
| 494 | Skilled Employer Sponsored Regional (Provisional) |
| 500 | Student (Primary visa holder = parent) |
| 500 | Student (exchange student) |
| 785 | Temporary Protection Visa |
| 786 | Temporary (Humanitarian Concern) |
| 790 | Safe Haven Enterprise |
| 820 | Partner |
| 870 | Sponsored Parent (Temporary) |
Other visa exemptions include:
- New Zealand citizens settling in Australia
- The child of the main application who is doing the doctoral program
- Child of a Masters by Research main application at a University in Regional Queensland
More information can be found at the site below.
DE International schedule of visa subclasses and enrolment conditions (qed.qld.gov.au)

Eligibility to access Medicare
In this column, we will look at the temporary visas that can apply for the Australian medical system, Medicare.
Medicare is a health care service for Australians that provides free treatment and hospitalization in public hospitals, low-cost medicines and free or low-cost care from doctors and other health professionals.
It is operated by the Australian Government, and Australian citizens and permanent residents can use free medical services.
There are many people who would like to receive the Medicare benefits. This is because those who hold a student visa or other temporary visas in Australia are required to purchase a medical insurance so that it meets the visa conditions. Medical insurances are quite expensive, ranging from about $100 to more than $300 per month for individuals, depending on the insurance benefits.
The following temporary visas are eligible for Australia’s Medicare services from the date of application.
- Temporary Partner Visa (subclass 820, 309)
- Skilled Work Regional Provisional visa (subclass 491)
- Skilled Employer Sponsored Regional Provisional visa (subclass 494)
- Witness Protection (Trafficking) Temporary visa (subclass 787)
- Support for Victims of People Trafficking Program
- Temporary Humanitarian Concern visa (subclass 786)
- Temporary or Permanent Parent Contributor Visa (subclasses 173, 143, 884, 864)
- Temporary Protection visa (subclass 785)
- Removal Pending Bridging visa (subclass 070)
- Unauthorised maritime arrivals holding a Bridging E (Class WE) visa
- Humanitarian Stay (temporary) visa (subclass 449), Ukraine nationals can read about Ukraine visa support on the Department of Home Affairs website
- Secondary Movement Offshore Entry visa XB (subclass 447)
- Safe Haven Enterprise visa (subclass 790)
All you need to prepare for Medicare enrolment is the Medicare enrolment form (MS004), a copy of your passport, and your current visa approval letter (or bridging visa approval letter)
For more information please visit:

[UPDATE] Health Examinations for Temporary Visa Applicants
The Department of Home Affairs has recently announced temporary changes to who is required to undertake health examinations.
After visa application, most Australian visas requested Health examination. However, due to the surg visa applicants, the Department of Home Affairs has announced that the medical examination will be waived for those applying for a visa within Australia.
These apply to the following visa subclasses and only if you are already in Australia:
· 401 Temporary Work (Long Stay Activity)
· 403 Temporary Work (International Relations)
· 405 Investor Retirement
· 407 Training
· 408 Temporary Activity
· 410 Retirement
· 417 and 462 Working Holiday
· 461 New Zealand Citizen Family Relationship (Temporary)
· 476 Skilled ‐ Recognised Graduate
· 482 Temporary Skill Shortage
· 485 Temporary Graduate
· 500 Students
· 590 Student Guardian
· 600 Visitor
· 870 Sponsored Parent (Temporary)
· 995 Diplomatic (Temporary)
However, a health examination is still required in exceptional cases.
- Have applied for a medical treatment, temporary protection, or a provisional visa
- Expect to incur medical costs or require medical treatment
- Are intending to work as (or study to be) a doctor, dentist, nurse or paramedic
- will enter a hospital, aged or disability care facility (if higher tuberculosis risk)
- are pregnant and intending to have the baby in Australia
- will work or train at an Australian childcare centre
- are aged over 75 years (if applying for a visitor visa)
- have had previous household contact with tuberculosis; or
- are requested to do so by the Department.
For those who have already scheduled a health examination with Bupa Medical Visa Services, the appointment may be cancelled and refunded. Bupa will send an SMS. Do not cancel the appointment by calling Bupa. The applicant should try to make it to the appointment even if they aren’t informed that it has been cancelled.
Generally, health examination depended on the nationality, past residence, level of tuberculosis risk your country poses, and intended length of stay. However, temporary visa applicants in Australia will not be required to undergo medical exams and chest x-rays to meet the health requirement.
Please look at the table below:
| Country risk level | Stay less than 6 months | Stay is 6 months or more |
| Low risk | No health examinations needed unless special circumstances apply | No health examinations needed unless special circumstances apply |
| High risk | No health examinations needed unless special circumstances apply | Medical examination and Chest x-ray (if aged 11 years or over) *Currently not applicable for temporary visa applicants already in Australia* unless special circumstances apply |
For instance, if you are Korean or Thai, these countries are considered to be high risk for tuberculosis included in the legislative instrument signed by the Minister of Home Affairs.
Therefore, if your stay will be 6 months or more you are required to undergo the medical examination and chest x-ray (if aged 11 or over) *.
In some situations, additional test is required if you intend to work or train to be a health care worker or work at a childcare centre, pregnant etc.
The appointment may be cancelled and refunded if the applicant has already scheduled a health examination with Bupa Medical Visa Services but have not yet shown up.
Please not that this is a temporary measure and applies to all eligible temporary visa applications currently with the Department and new applications made in Australia. The Government will review these arrangements in early 2023.
Please see the Department of Home Affairs website for further details.
Who needs health examinations (homeaffairs.gov.au)

Checking my VISA details with VEVO
This column will look at how to check my VISA details with VEVO.
With VEVO you can check the visa details and conditions of your current visa.
You will be able to see the visa type, visa status, expiry date and the visa conditions.
Step 1. Things you need
- Passport
- Visa Grant Letter OR Transaction Reference Number (TRN)
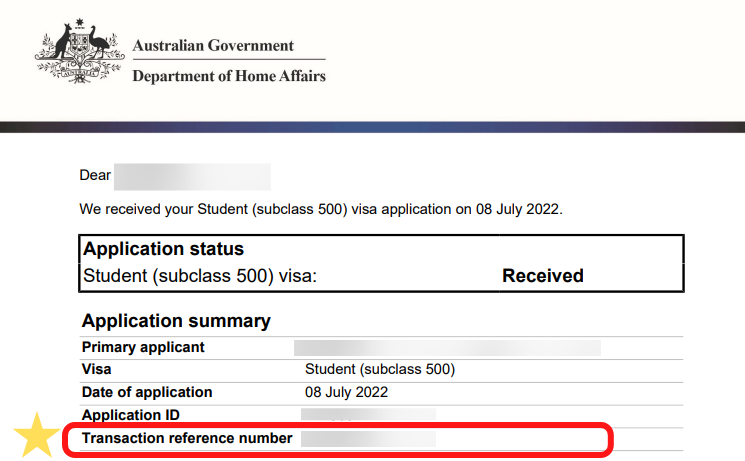
What is my Transaction Reference Number (TRN)?
The Transaction Reference Number is the reference number you receive after applying your visa application.
Please see below image.
Where is my Visa Grant Number?
The Visa Grant Number is on the Visa Grant Letter.
Please see below image.

Step 2. Access VEVO website
Check visa conditions online (VEVO) (homeaffairs.gov.au)
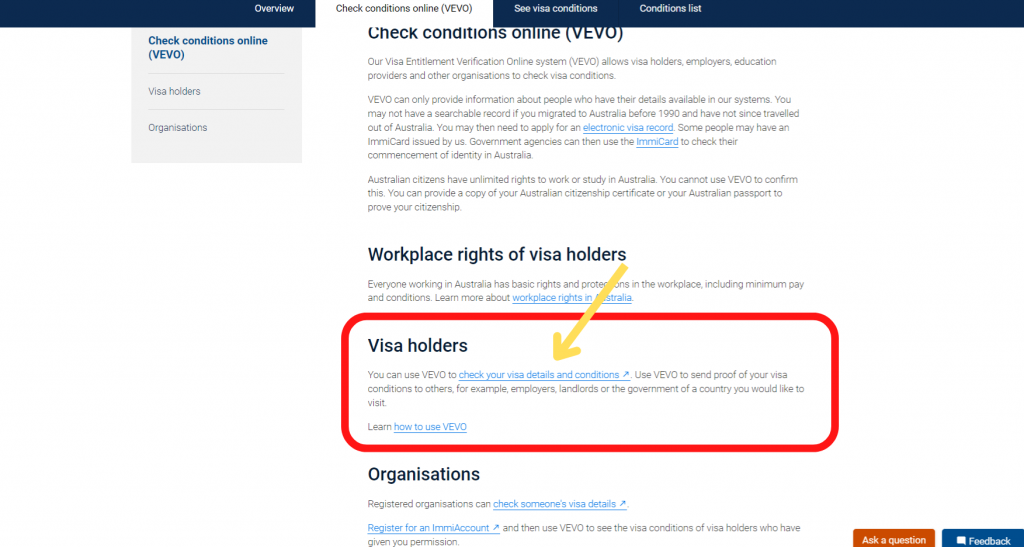
Select ‘Check your own visa details and conditions’ under Visa Holders
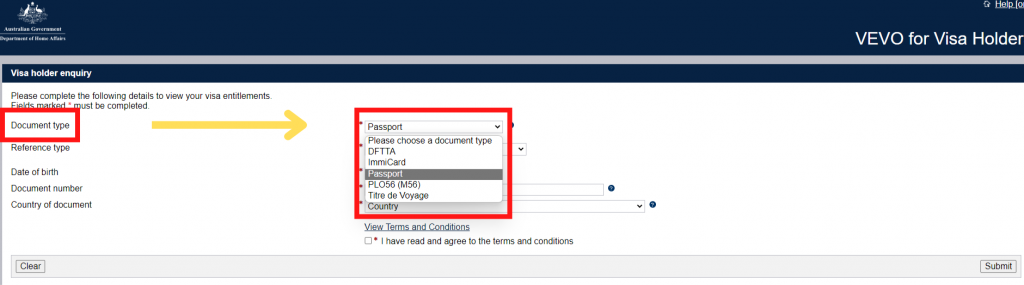
Step 3. Select the Type of travel document to passport
Step 4. Select Transaction Reference Number (TRN) OR Grant Number for Reference Type
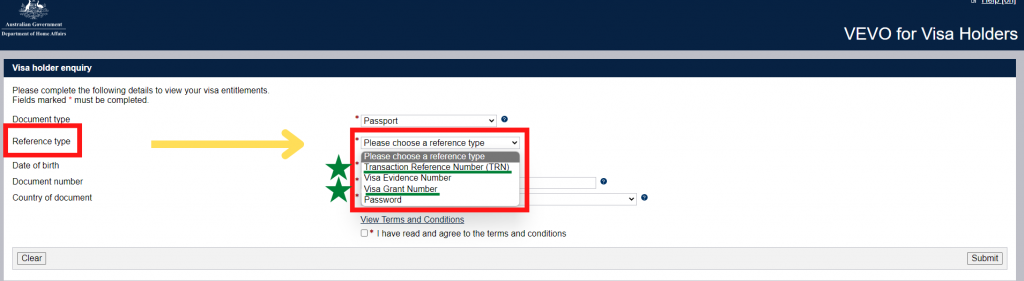
If your visa is not approved yet, you have to use the Transaction Reference Number (TRN)
Step 5. Insert your TRN or Visa Grant Number and enter personal information
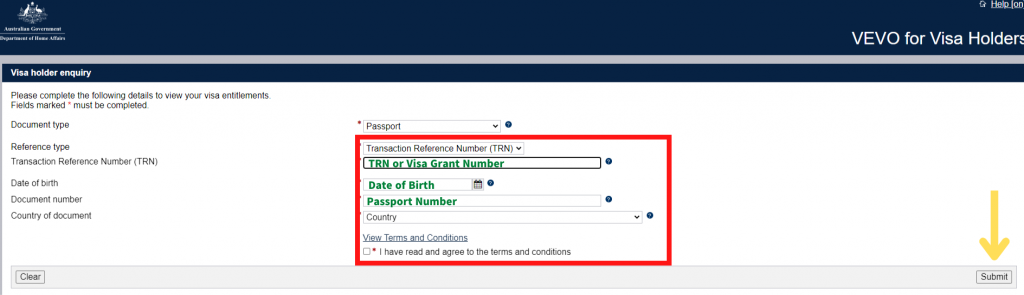
After all details are inserted click Submit
Step 6. Your Visa Status should come up like below
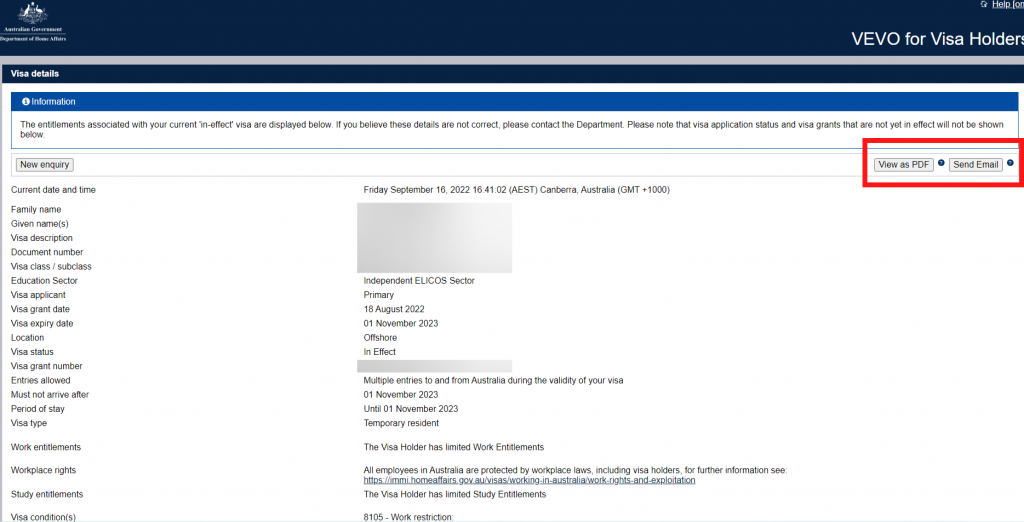
You can View as PDF or Send email and keep a copy of your visa status.

Temporary Activities 407 Sponsor Obligations
This column will look at the obligations the employer (sponsor) must comply with for the Training visa, subclass 407.
Sponsorship obligations are different for all visas.
For example, the TSS Visa Subclass 482 which also requires a sponsorship, is for the Standard Business Sponsorship (SBS).
On the other hand, The Training visa subclass 407 is for the Temporary Activity Sponsorship. Therefore obligations for the employer are applied differently.
You can see from the table below that the obligations are slightly different depending on the visa subclass.

407 Sponsorship Obligations
2.78 Cooperating with Inspectors
Employers are required to cooperate with Workplace Inspectors. The inspector powers set out in Subdivision F of Division 3A of Part 2 of the Migration act are to:
- Enter business premises or other paces
- Inspect any work, process or object
- Interview any person at an entered premises or place
- Access and make copies of records and document that are kept in premise
- Request for evidence for correctness
2.81 Costs to Commonwealth – To locate and remove an unlawful non-citizen
This obligation is to pay costs incurred by the commonwealth if the 407-visa holder overstays their visa. It only covers costs incurred when the person becomes illegal. A maximum limit of $10,000 is applicable for this obligation.
2.82 Maintenance of records
The employer is obliged to keep certain records for 5 years.
This obligation ends 2 years after the first day on which each of the following occurs:
- The person ceases to be an approved work sponsor or party to a work agreement
- There are no primary sponsored persons employed by the sponsor
- Request for payment of return travel costs
- Details of payment of return travel costs – date, who for, amount
- Details of how the sponsor complied with the requests
- The sponsor ceases to hold the required licence referred
2.83 Provide records and information to the Minister
An authorised departmental officer (as the Minister’s delegate) can request the following information:
- Records that the person is required to be kept under a law of the Commonwealth or State or Territory
- Records required to be kept under regulation
- Work agreement, records or information related to the administration of the work agreement.
2.84 Provide information to the Immigration, Department of Home Affairs
The employer must notify the Department of Home Affairs of certain events:
- Changes to the legal structure of the employer
- If the primary sponsored person fails to participate in the activity which their visa was granted
- the primary sponsored person ceases participation
- Payment of return travel costs of the primary sponsored person
- Cessation or expected cessation of primary sponsored person
2.85 Secure an offer of a reasonable standard of accommodation (In relation to a volunteer role only)
The employer must provide the following to the sponsored person:
- A reasonable standard of accommodation
- Ensure that the sponsored person has accommodation in Australia
Volunteer role, according to sub-regulation 2.57(5) is the following:
- Not receive remuneration for performing the duties of the position other than:
- Reimbursement for reasonable expenses incurred by the person in performing the duties
- Prize Money
- An Australian worker would not otherwise carry out the duties in return for wages.
2.86 Ensure that the primary sponsored person work or participates in the activity in relation to which the visa was granted
2.87 Not to recover, transfer or take actions resulting in another person paying for certain costs.
The employer must not seek to recover or have another person pay for the cost of:
- Obtaining sponsorship approval
- Recruitment of the primary sponsored person

Temporary Sponsored Parent (subclass 870) Visa Conditions
In this column, we will look at the visa conditions for the Temporary Sponsored Parent visa.
The Temporary Sponsored Parent visa was introduced in 2019 and is a visa where parents of Australian Permanent Residents or citizens can legally stay in Australia for a certain period.
We also happen to have a temporary parent visa approval today, just in time to introduce the visa conditions.

If you look at the Visa approval letter from the Department of Home Affairs, the visa period is stated on page 1, and pages 2 to 5 are where the conditions are announced.
It is essential to read the conditions carefully in order not to cause problems with the visa.
Temporary Sponsored Parent (subclass 870) Visa Conditions
▶No work (visa condition 8103)
This condition means that you are not allowed to undertake work in Australia.
However, you can apply for a Tax File Number (TFN) as you are considered a tax resident.
▶ Activity limitation (visa condition 8303)
This condition means that you must not become involved in activities disruptive to, or violence threatening harm to the Australian community or a group within the community.
▶ Maintain health insurance (visa condition 8501)
This condition means that you must maintain adequate health insurance in Australia.
Health insurance depends on personal health conditions and different insurance companies but is generally from $230 a month.
▶ Must leave before visa expiry (visa condition 8531)
This condition means that you are not allowed to stay in Australia beyond the period of stay permitted by your visa.
▶ Must not engage in criminal conduct (visa condition 8564)
This condition means that you must not engage in criminal conduct during your stay in Australia.
▶ Notify new details (visa condition 8609)
This condition means that you must notify us within 14 days after any change to your personal or contact details (name, address, phone number, email address, passport). You must do this in writing and can use Form 1022 Notification of changes in circumstances (Section 104 of the Migration Act 1958), which is available at Overview (homeaffairs.gov.au)
Let’s look at the visa application process, cost and processing times.
Visa Application Process
There are two processes for the Temporary Sponsored Parent visa.
Step 1: Sponsorship Application
A child who is an Australian Citizen or a permanent resident applies for a sponsorship application.
Step 2: Parents apply for the Temporary Sponsored Parent visa subclass 870
Both sponsor/ visa applicants must meet the eligibility criteria to apply.
Visa Cost
- Sponsorship Application – $420
- Temporary parent visa up to 3 years – $5,090
- Temporary parent visa up to 5 years – $10,000
The visa application charge is payable in two instalments, with one payment at the time of application and the remainder paid prior to visa grant.
(As of August 12, 2022)
Processing times
As for visa processing times, it may take a minimum of 3 months to complete the visa process after receiving the sponsorship approval.
This is the current visa processing period listed in the Department of Home Affairs.

According to the announcement in August 2022, unlike the Contributory Parent visa and Parent visa, which can take from 40 months to a maximum of 30 years, the Temporary Sponsored Parent (subclass 870) visa has the advantage of faster visa processing. It allows you to stay in Australia for up to 10 years, with the requirements not being too strict.
Moreover, sponsors do not require Family Balance Test condition when applying for a Temporary sponsored parent visa. Regardless of the number of siblings, just at least one child must be living in Australia after obtaining permanent residence or citizenship, with a minimum income of AUD 83,454.80 (standard set by the Ministry of Immigration, as of August 12, 2022,), can apply for sponsorship.
If you have any further questions about the temporary parent invitation visa requirements or would like to consult, please contact Mosaic Migration.

How long do I have to wait for a Parent Visa?
This column will be about the new announcement of visa processing times for Parent visas.
According to the Department of Home Affairs, due to the COVID-19 Pandemic, visa processing has been significantly delayed.
Even in our clients’ case, as there were travel restrictions after the COVID-19 Pandemic, there were many inquiries about Parent visas to invite them to Australia. Due to COVID, many people in Australia cannot meet their parents abroad for at least 2-3 years.

The summary of the announcement is as follows.
As of 30 April 2022, they have released for final processing:
- Contributory Parent visa applications with a queue date up to July 2016
- Parent visa applications with a queue date up to October 2010
- Aged Parent visa applications with a queue date up to December 2012
The Department is required to process Parent and Contributory Parent applications in date order and within annual limits. The current onshore and offshore processing times in both Parent and Contributory Parent categories are very different, and the Department has announced that it is taking action to correct them.
→ Onshore Contributory Parent (Subclass 884 and Subclass 864) visa subclasses have been assessed up to February 2017. Onshore Contributory Parent visas lodged from February 2017 onwards will likely take longer to process to bring the offshore applications back to parity.
→ Onshore Aged Parent (Subclass 804) visas have been assessed up to Queued Date of December 2012. Onshore Aged Parent applications with a Queued Date of December 2012 are likely to take longer to process to bring the offshore applications back to parity.
→ All Contributory Parent visa applications lodged before 1 June 2018 have been given a queue date of the application lodgment date, and applications lodged on or after 1 June 2018 are assessed and given a queue date when it meets the initial visa criteria.

Processing times
- New Contributory Parent visa applications lodged that meet the criteria to be queued are likely to take at least 67 months to be released for final processing.
- New Parent and Aged Parent visa applications lodged that meet the criteria to be queued are likely to take at least 30 years for final processing.
According to the announcement, people feel inconvenienced and dissatisfied because even though the Contributory Parent Visa requires a contribution of $50,000, it takes 5-6 years. And the Parent Visa takes up to 30 years.
Regarding visa processing time, the new Temporary Parent Visa (subclass 870) introduced in 2019 may be a better option. The Temporary invitation visa allows you to stay in Australia for up to 10 years.
A temporary Parent Visa (subclass 870) has different requirements from Parent Visas, so if you have any questions regarding the temporary parent visa, please get in touch with Mosaic Migration & Education. We will guide you in detail.

Temporary Changes to subclass 485 Graduate Visa
According to the new rules and regulations, there has been an announcement on the temporary changes to the Australian Graduate 485 Visa (Graduate work stream).
Changes in requirements for Temporary Graduate 485 visa has come into effect from 1 July 2022.
What is the subclass 485 visa?
The subclass 485 visa is a visa that allows you to reside in Australia temporarily after completing your studies in Australia.
Before 1 July 2022, only Medium-long Term skills occupation and the requirement of applying for the provisional skilled assessment was needed to satisfy the conditions of the 485 Visa Graduate work Stream.
However, From 1 July 2022
You only need to meet the Australian study requirement!
This is great news for students as they can obtain a graduate visa in Australia for up to 2 years and can be a pathway to apply for the permanent residence.
Conditions before 1 July 2022
- Medium-Long Term Skills occupation generally Diploma graduates who have completed Commercial Cookery, Early Childhood education, Automotive Maintenance and Carpenter etc.
- Provisional Skilled Assessment
- Under 50 years old
- English requirements 6.0 or higher based on IELTS (5.0 or higher in each area), other recognised English tests are TOFEL iBT, PTE Academic, OET, Cambridge C1 Advanced
Changes from July 1, 2022 until June 30, 2023
- No Occupation nominated required
- No Provisional Skills assessment required
As long you meet the Australian Study Requirements, you can become a 485-visa applicant!
What are the Australian Study Requirements?
(Australian Study Requirements can vary on individual circumstances)
01. Course Requirements
- be either a Bachelor’s degree or higher, a diploma, an advanced diploma, or a trade qualification
- have been undertaken at an Australian educational institution in Australia
- have been taught in English
- be registered on CRICOS
- have been undertaken while you held a visa authorising you to study
- Note: You cannot use English language proficiency courses or enabling programs to meet the Australian study requirement.
02. The Academic Years Study Requirements
- be either a Bachelor’s degree or higher, a diploma, an advanced diploma, or a trade qualification
- have been undertaken at an Australian educational institution in Australia
- have been taught in English
- be registered on CRICOS
- have been undertaken while you held a visa authorising you to study
- Note: You cannot use English language proficiency courses or enabling programs to meet the Australian study requirement.
03. Minimum of 16 months study in Australia
The Australian study requirement cannot be met in less than 16 calendar months.
The above temporary changes will take effect from July 1, 2022, and will last until June 30, 2023, with the possibility of extension.
Subclass 485 visa application must be made within 6 months from the course completion date.
Conditions may vary slightly depending on individual circumstances so contact us for a consultation, or if you have any questions about visa requirements for Australian graduates, please contact Mosaic Immigration!

Partner Visa: Important Points
This column will learn about the Partner Visa subclass 820/801 (onshore) and 309/100 (offshore).
Subclass 820/801 (Onshore) – Applying in Australia
Subclass 309/100 (Offshore) – Applying outside Australia
Partner visa number changes depending on the location of the applicant when applying for a visa, and there are pros and cons in the two visa types.
If applying within Australia (onshore), the applicant must hold a substantive visa at the time of application.
*Substantive visas are all visas except bridging visa, criminal justice visa and enforcement visa*
For onshore applications, a bridging visa is issued, and even before a permanent residency is granted, they can receive Australian Medicare benefits while waiting for the visa grant.
A partner visa requires the applicant to have a genuine relationship with an Australian citizen, permanent resident, or an eligible New Zealand citizen. The relationship must continue until the date the visa is granted.
*Exceptions apply (Domestic Violence, Partner passed away etc.)*
So, what is a Partner relationship, and how do we prove it?
The Australian Immigration law divides partner relationships into Spouse and De Facto relationships.
A spouse Relationship is when you are legally married and,
A De Facto Relationship is a Common-law relationship and generally requires that you have lived together for at least 12 months and maintained an exclusive relationship.
For a De Facto relationship, a Civil Partnership Registration Certificate is often used as an alternative to the 12-month residency requirement.
It would be nice if a Marriage Certificate or a Civil Partnership Registration Certificate could prove a Partner relationship. Still, as required by the Australian Immigration Law, you must submit sufficient supporting documents for the four types below to prove a genuine relationship.
- Financial Aspects of the relationship
- Nature of Household
- Social Aspect of Relationship
- Nature of commitment to each other
There are cases in which the visa examination is delayed or rejected if there are insufficient supporting documents for the four types.
Examples of specific evidence for the four types are:
| Financial aspects of the relations | · Joint mortgage or lease documents · Joint loan documents for major assets like homes, cars, or major appliances · Joint bank accounts Statements · Household bills in both names |
| Nature of Household | · Household bills in both names · Mail or emails addressed to you both · Documents that show joint responsibility for children · Documents that prove your living arrangements |
| Social Aspect of Relationship | · Joint invitations or evidence you go out together · Proof you have friends in common (group photos) · Proof you have told government, public or commercial bodies about your relationship · Proof you do joint sporting, cultural or social activities together · Proof you travel together |
| Nature of commitment to each other | · Proof you have knowledge of each other’s background, family situation or other personal details. · Proof you have combined your personal matters · The terms of your wills · Proof you stay in touch when apart |
Other evidence includes a statement of relationship, Form 888 (from two or more people who are Australian citizens or permanent residents), photos and travel records.
The Partner visa is not a simple visa that can be granted just with the fact that the applicant and sponsor is married or in a Common-law marriage.
Please contact us if you are preparing for a partner visa and need professional advice.
In the next column, we will take a closer look at the points to be aware of when applying for a partner visa through real cases in which the partnership was maintained, but the visa was rejected.
